Your location:

Product classification of Meiyan One Pump Valve
- ShangHai Meiyan Yi Pump & Valve Co.,LTD.
- Sales hotline:
+86 21 5640 2009 - Pump customer service:
+86 138 1691 3072 - Valve customer service:
+86 1381 6913 072 - E-mail:
my1pv@1bengfa.com
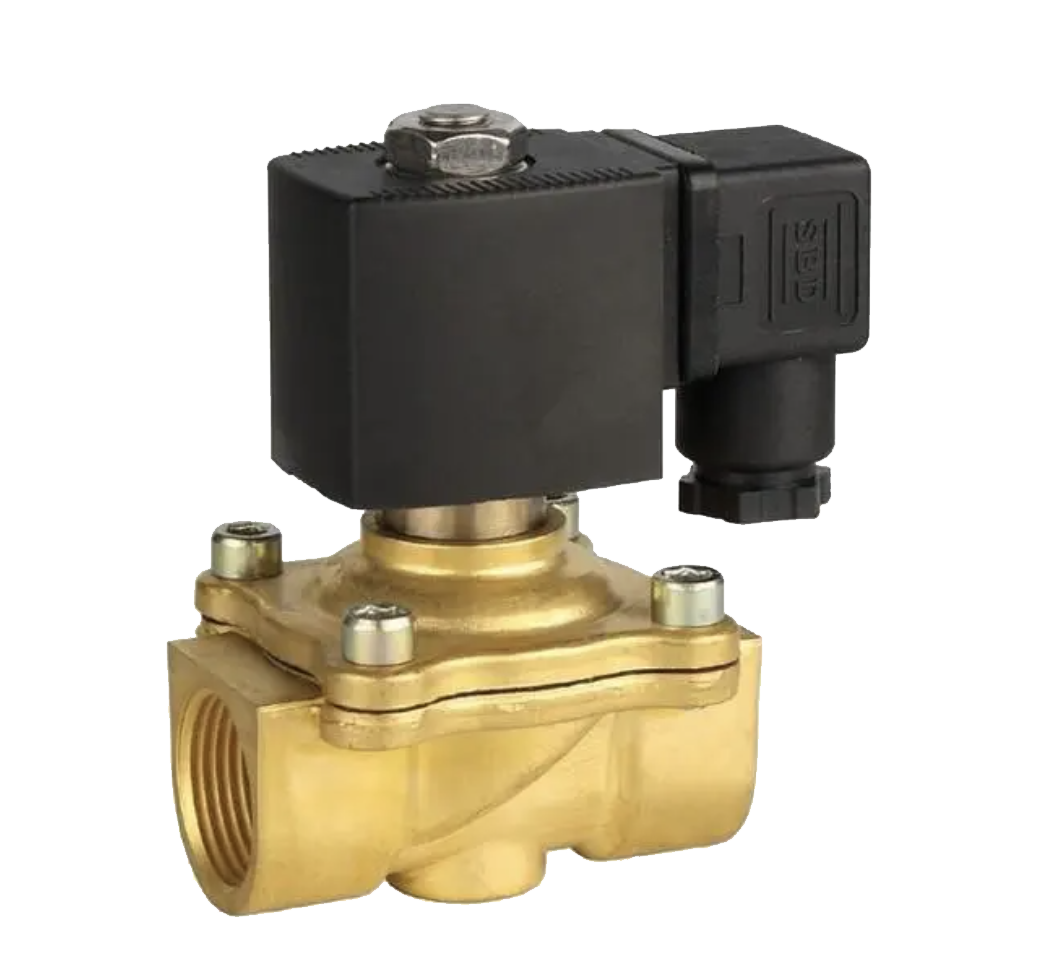
Solenoid valve
Solenoid Valve mainly rely on the electromagnetic force generated by the power supply coil to drive the iron core to open and close the valve disc. Generally, solenoid valves are in a normally closed (or normally open) state before being powered on. After being powered on, the electromagnetic force of the coil drives the movable iron core, causing the valve to immediately open (or close). The main characteristics of the solenoid valve produced by Shanghai Meiyan Yipum Valve are rapid opening and closing action, simple structure, and easy operation. It is mainly used for automatic cut-off, connection, or switching of fluid flow direction. There are various structures of solenoid valves, generally divided into two types: unfilled and filled. Non filled solenoid valves do not require packing sealing, and the casing is filled with fluid. In addition to general fluids, they are more suitable for valuable or toxic fluids such as helium, fluorocarbons (see refrigerants), and ammonia. Filler type solenoid valves are mostly used for high temperature, low temperature, or highly corrosive fluids due to the use of fillers that do not come into contact with the casing and iron core. However, due to the presence of a stuffing box, the volume is relatively large and increases the friction force of the valve stem movement. The power supply of solenoid valves can be divided into AC and DC. The action of electromagnetic valves using alternating current is particularly fast, but it is prone to heating and has a small opening and closing force. Electromagnetic valves using direct current are less prone to heating and have greater opening and closing force, but their action is not as fast as alternating current. Electromagnetic valves can be divided into various specifications and models such as normally closed, normally open, pilot operated, high-temperature, two position three-way, two position five way, etc. The following product pictures are for reference only.
-
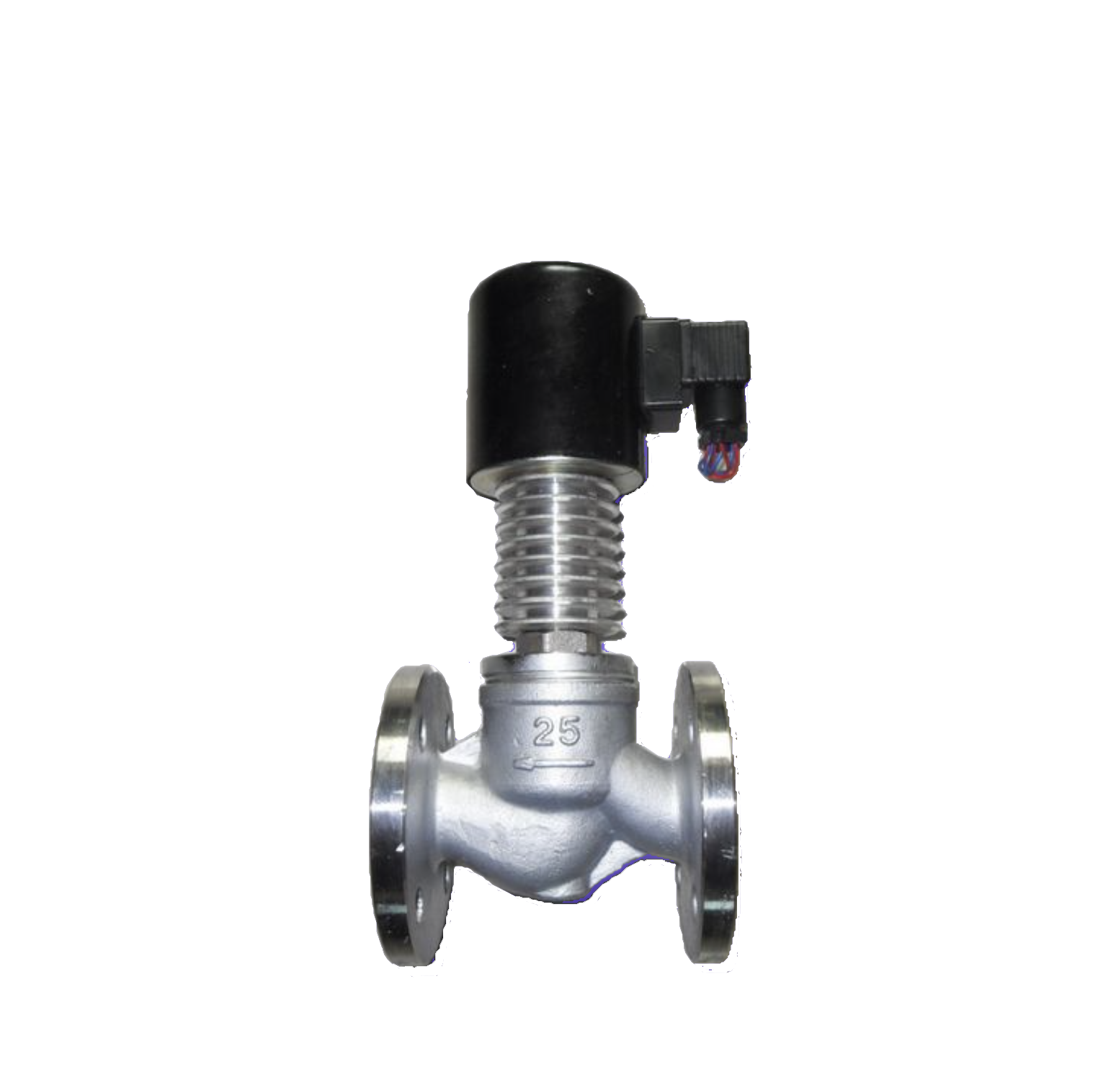

Steam solenoid valve
Steam solenoid valve controls the opening or closing of the valve core through the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnetic coil on the valve, thereby achieving precise control of the steam flow through the valve channel. The working principle of steam solenoid valve is mainly based on the design structure of the solenoid coil, valve core, spring, and valve seat of the valve. The working principle of a normally closed steam solenoid valve is that when current passes through an electromagnetic coil, the coil generates electromagnetic force that attracts the valve core to move, thereby opening the flow channel. When the current is disconnected, the electromagnetic force disappears, and the valve core resets under the action of spring force, closing the flow channel. The working principle of a normally open steam solenoid valve is exactly opposite to that of a normally closed one. The steam solenoid valves produced by Shanghai Meiyanyi Pump Valve are mainly suitable for steam pipelines, with stable performance. New and old customers are welcome to choose.View details>>
-
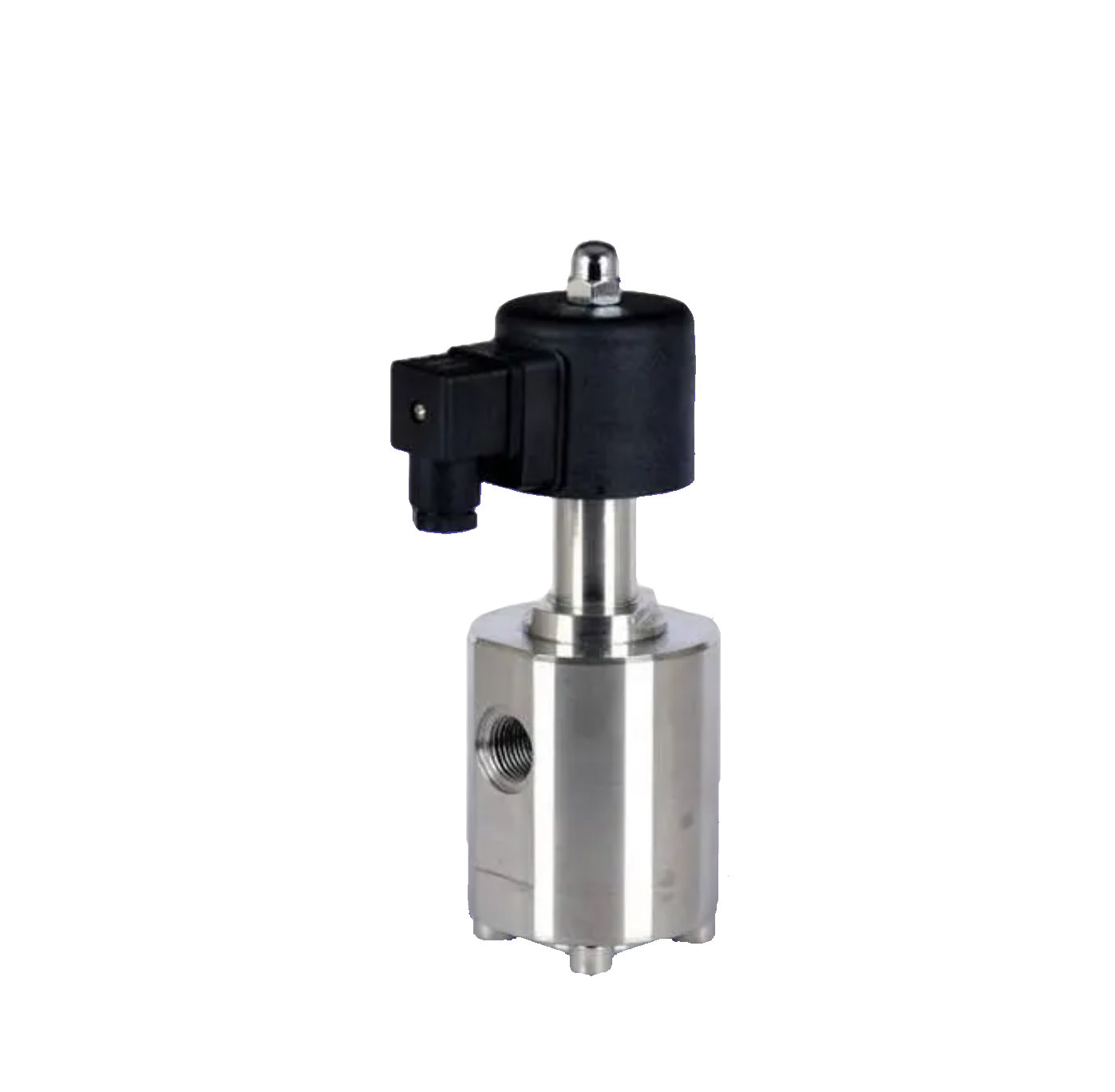

High pressure solenoid valve
High pressure solenoid valve refers to a specialized solenoid valve used for high-pressure pipelines. It is generally selected for pipeline equipment with a pressure of PN40 or above. High pressure solenoid valves play an important role in industrial control systems and can be used to quickly adjust the direction, flow rate, velocity, and other parameters of high-pressure pipeline media. The different types of high-pressure solenoid valves produced by Shanghai Meiyanyi Pump Valve are suitable for different industrial fields, such as hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, and automation equipment, ensuring precise control and efficient operation of the system. High pressure solenoid valves have both step-by-step direct acting and pilot operated designs, which combine different working principles and technical characteristics to adapt to the working conditions and requirements of different high-pressure pipelines.View details>>
-
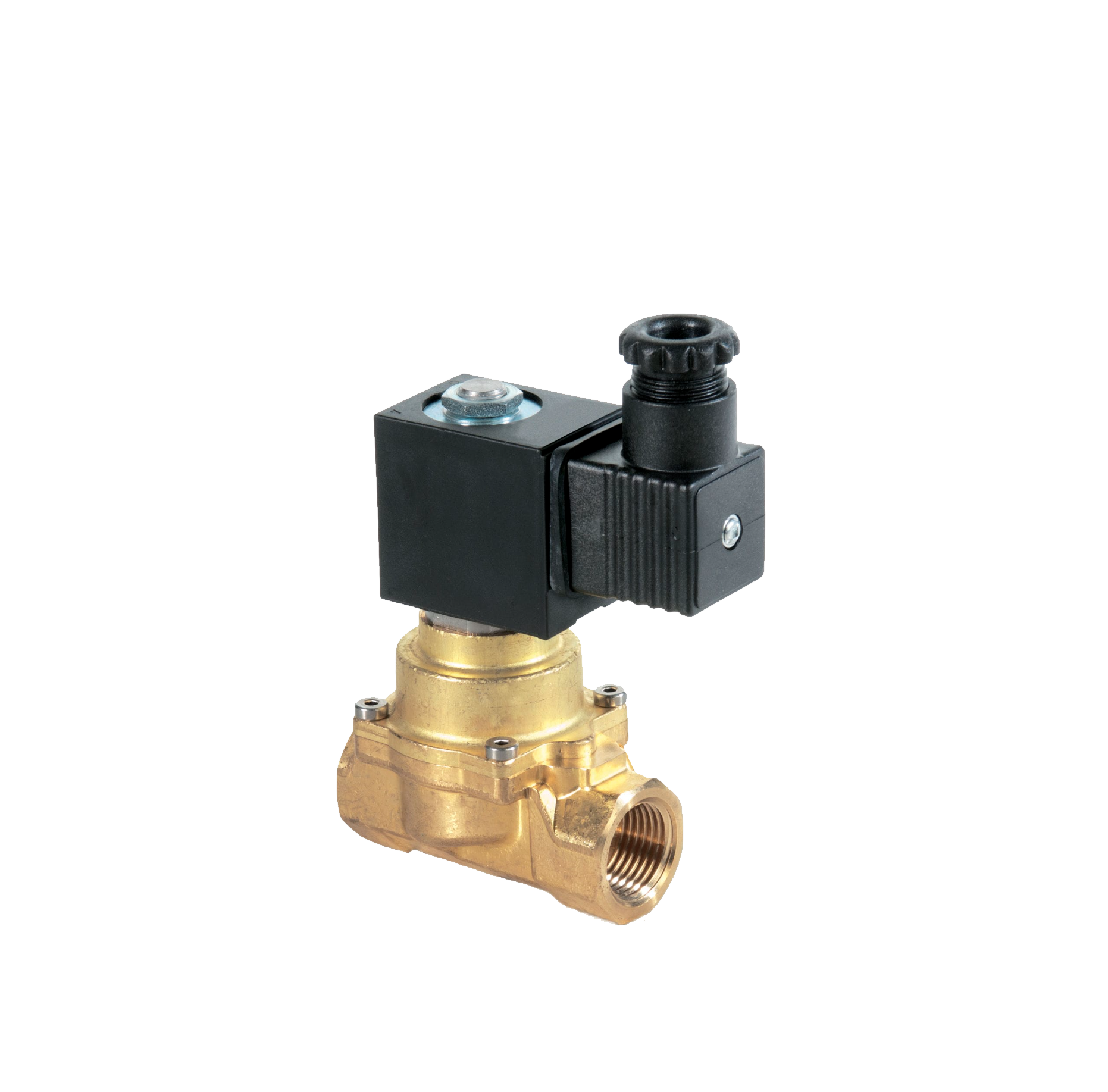

Micro Electromagnetic Valve
Micro solenoid valve refers to a smaller diameter solenoid valve, mainly used as a common electromagnetic control component, widely used in various mechanical and automation equipment. It consists of two parts: an electromagnet and a valve body. The magnetic field generated by the electromagnet attracts the iron core on the valve body, thereby realizing the principle of valve opening and closing control. The miniature solenoid valve of Shanghai Meiyanyi Pump Valve is used in various industrial control systems to control parameters such as fluid direction, flow rate, and speed. They can be combined with different circuit designs to achieve precise and flexible control. Micro solenoid valves have the characteristics of safety, convenience, diverse models, and wide applications, making them an indispensable component in the field of industrial automation. They are suitable for industries such as generator sets, diesel engines, analytical instruments, and medical devices.View details>>
-
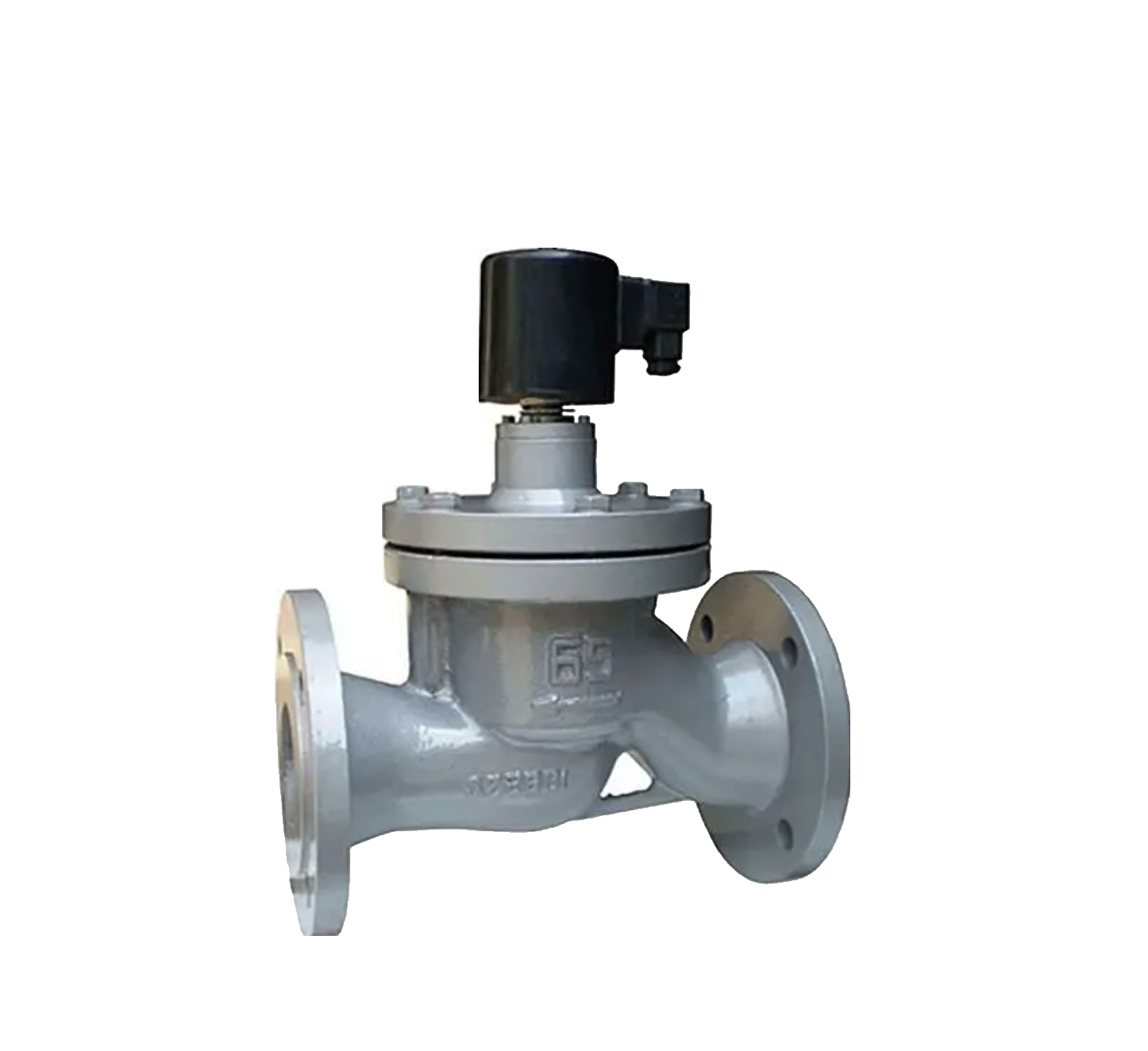

Pilot operated solenoid valve
When the pilot operated solenoid valve is powered on, the electromagnetic force of the coil will lift the valve stem, open the pilot valve port, and release the pressure in the upper chamber of the solenoid valve through the pilot hole, thus forming a high and low pressure difference around the main valve core. This pressure difference causes the fluid pressure to push the main valve core upwards, opening the main valve port. When the solenoid valve is powered off, the spring force and the gravity of the main valve core will reset the valve stem, close the pilot hole, and the main valve core will move downward to close the main valve port. At this point, the pressure in the upper chamber of the solenoid valve increases, and the fluid pressure pressurizes the main valve core, ensuring better sealing. The pilot operated solenoid valves produced by Shanghai Meiyanyi Pump Valve are widely used in key systems such as high temperature and high pressure in industrial automation control. Welcome new and old customers to call or write to inquire about solutions.View details>>
-
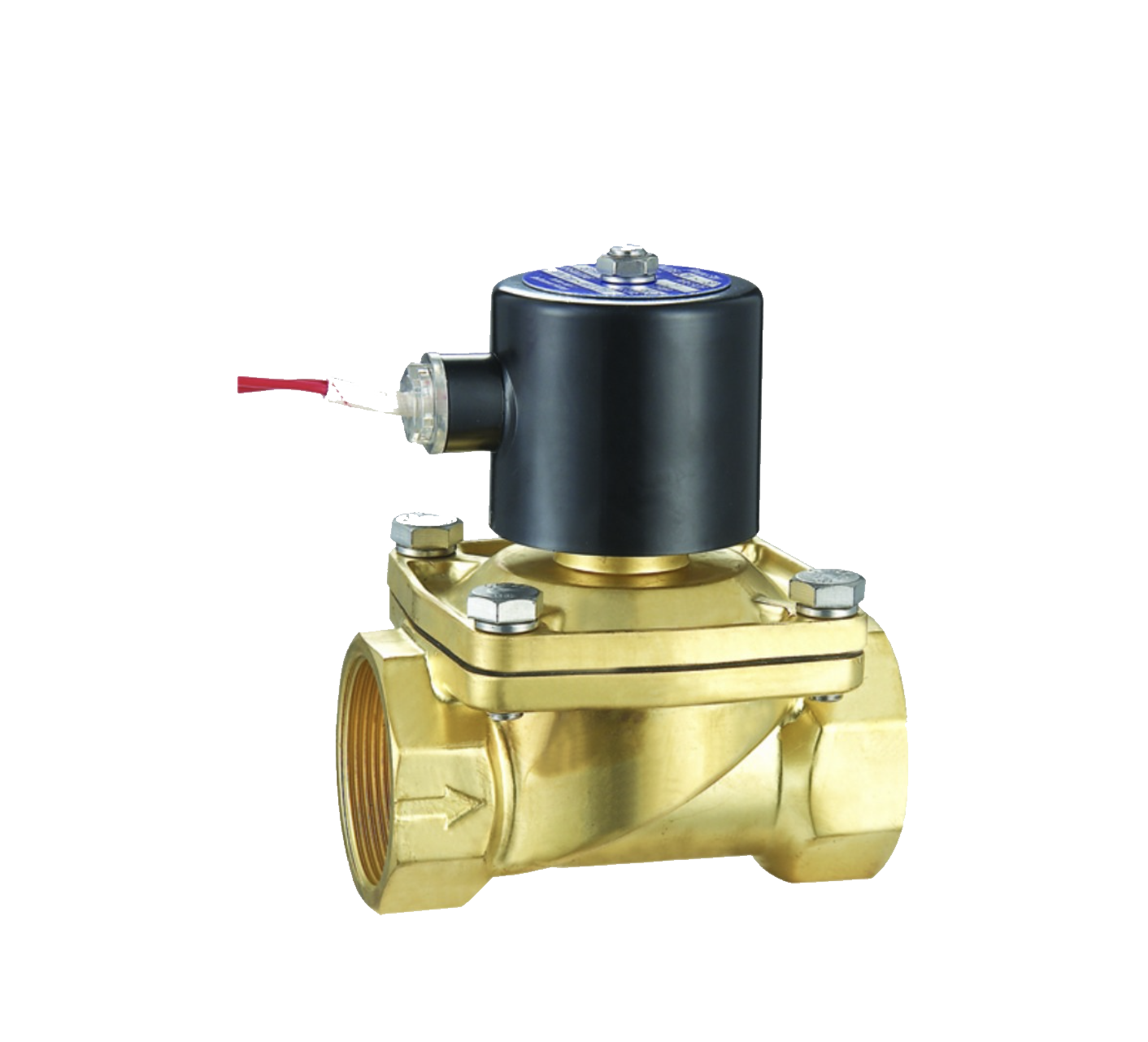

Direct acting solenoid valve
The working principle of a direct acting solenoid valve can be summarized as follows: when powered on, the solenoid coil generates electromagnetic force, lifts the closing member from the valve seat, and opens the valve; When the power is cut off, the electromagnetic force disappears, and the spring presses the closing member against the valve seat, causing the valve to close. This type of solenoid valve can work normally under vacuum, negative pressure, and zero pressure, but the diameter generally does not exceed 25mm. The direct acting solenoid valve produced by Shanghai Meiyanyi Pump Valve is simply controlled by the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnetic coil to open and close the valve core, thereby achieving precise control over the flow rate and direction of the fluid. Direct acting solenoid valves can be used with different circuits to achieve desired control, and have the characteristics of safety, convenience, fast opening and closing, multiple models, and wide applications. Welcome new and old users to make purchases.View details>>
-
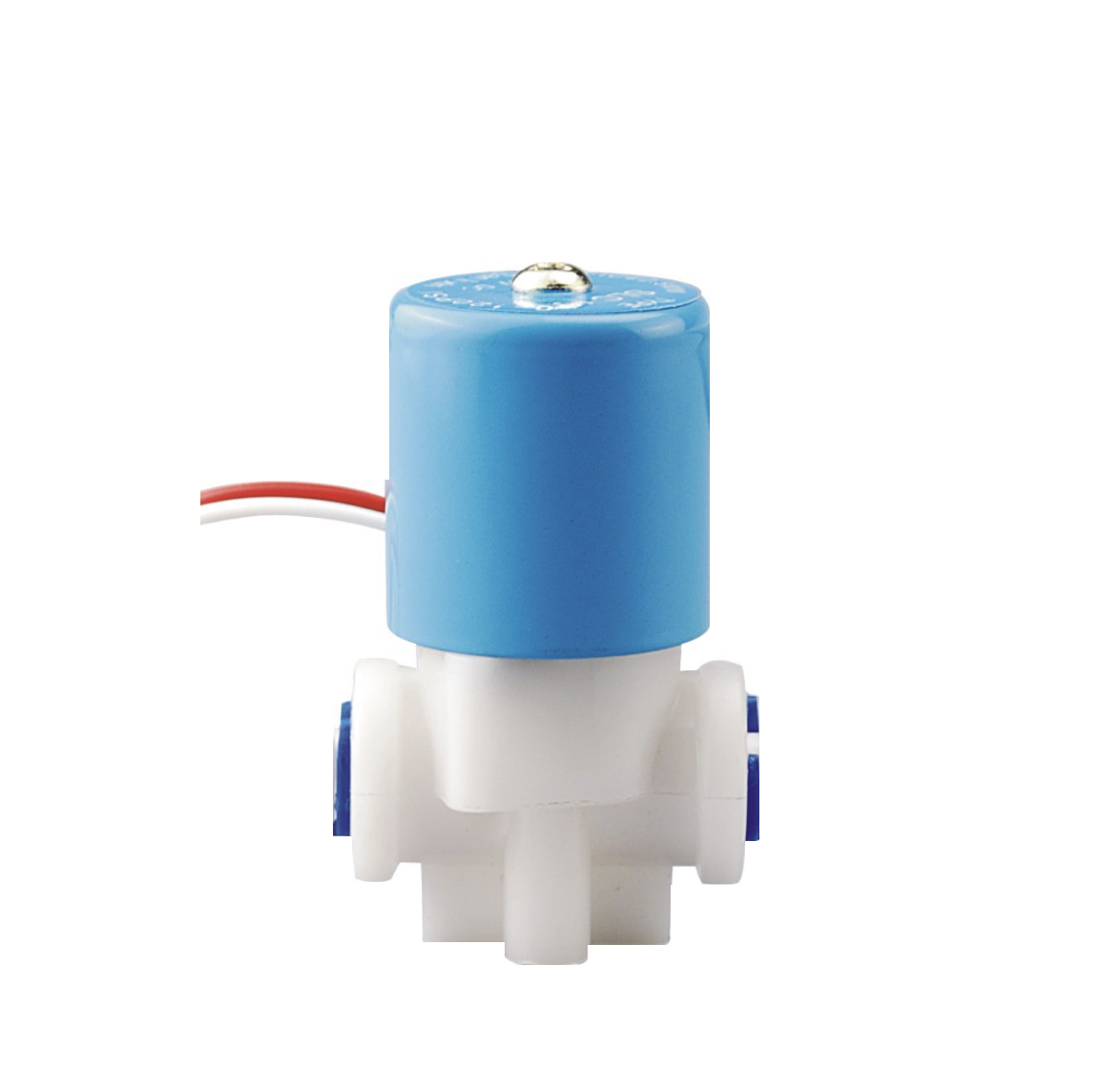
Water dispenser solenoid valve
The water dispenser solenoid valve is a device used in the water dispenser control system, which is controlled by the electromagnetic effect of the coil and can be used to adjust the direction, flow rate, speed, and other parameters of the medium. The main function of the water dispenser solenoid valve is to accurately control the water output of the water dispenser. Generally, the solenoid valve switch is controlled based on the size of the water supply pipe of the water dispenser and read seconds through a timer. The water dispenser solenoid valve produced by Shanghai Meiyan Yi Pump Valve has the characteristic of fast response, which can quickly respond to water supply needs in a short period of time and improve the stability and reliability of the water supply system. Water dispenser solenoid valves are generally made of small-diameter PVC material, which has the characteristics of light weight and high sensitivity.View details>>
-
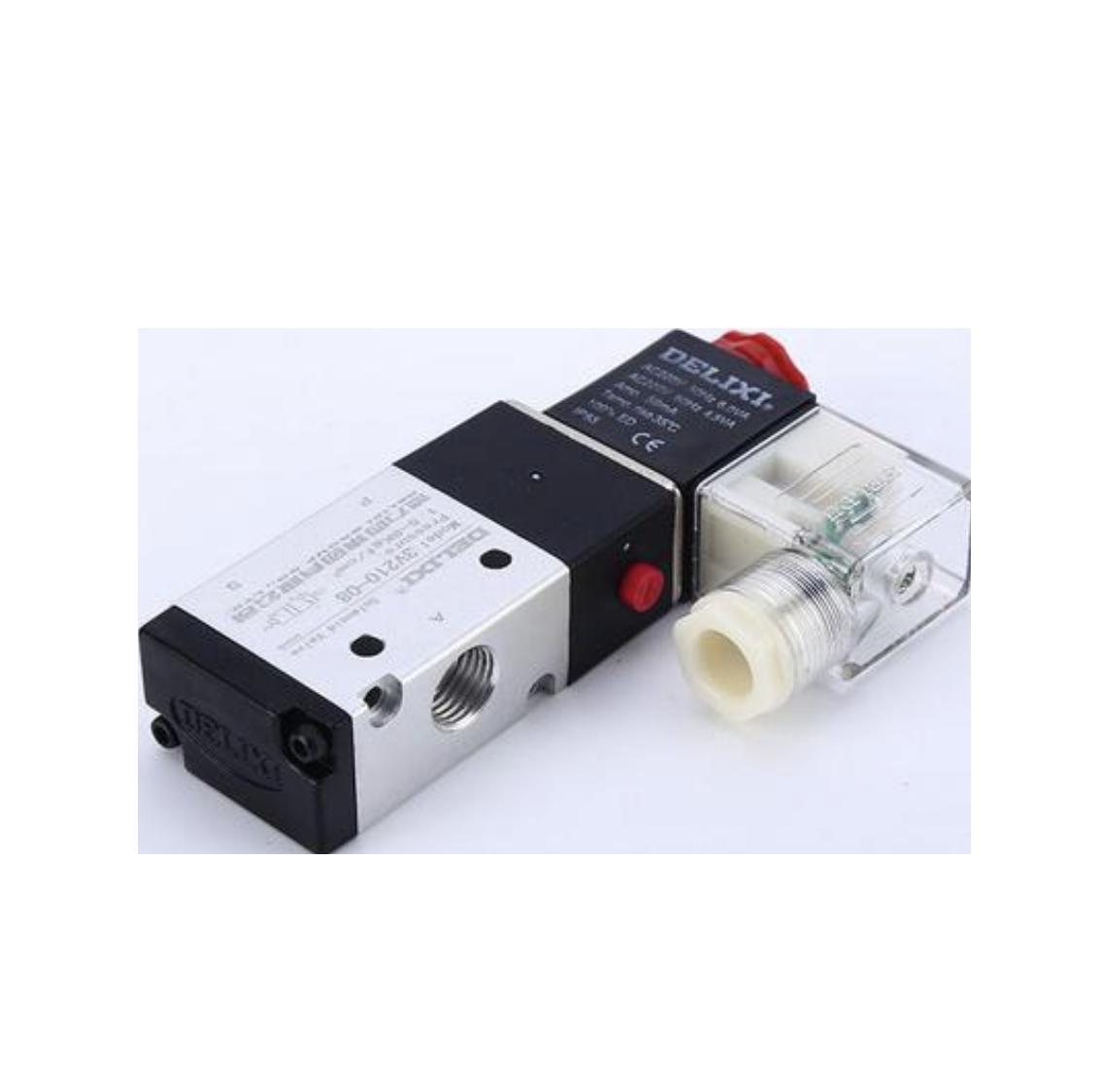

Two position three-way solenoid valve
The two position three-way solenoid valve is controlled by a double coil. One coil is instantly powered on and then the power is turned off and the valve is opened, while the other coil is instantly powered on and then the power is turned off and the valve is closed. It can be kept closed or open for a long time, which can prolong the lifespan of the coil. Best used in high-temperature pipelines. The two position three-way solenoid valves produced by Shanghai Meiyan Yi Pump Valve are widely used in various fields such as metallurgy, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, tobacco, food and medical, urban construction and environmental protection, water supply and drainage, heating and air conditioning, fire safety, scientific research, and energy-saving industries. A two position three-way solenoid valve is a control valve with two working positions and three channels. It changes the working position of the valve by energizing and de energizing the electromagnet, thereby controlling the flow direction of the medium. Two position three-way solenoid valves are widely used in control systems for liquids and gases, with advantages such as simple structure, high control accuracy, and fast reaction speed.View details>>
-
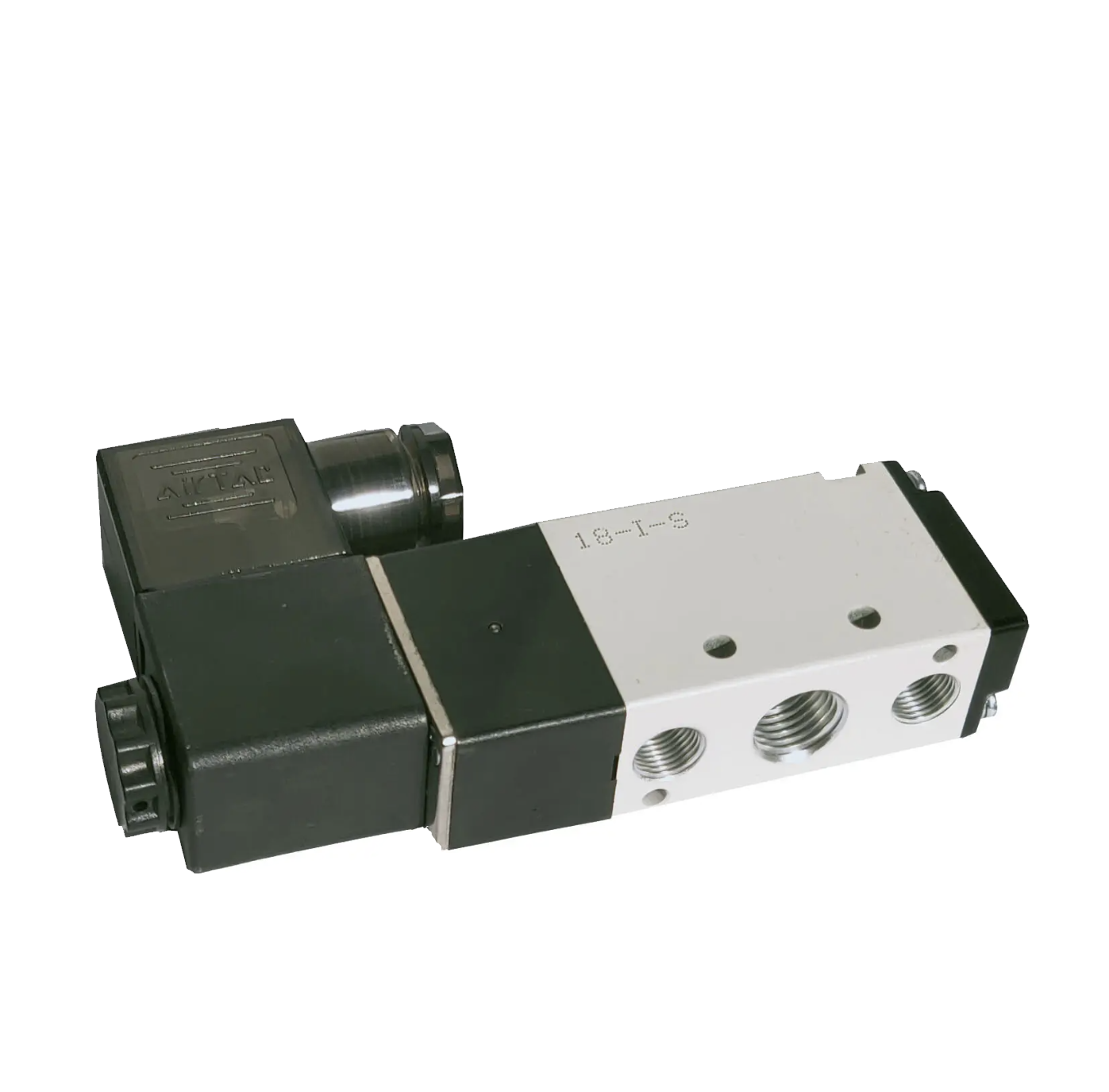

Two position five way solenoid valve
The two positions of the two position five way solenoid valve refer to the two working positions of the solenoid valve core: when the solenoid valve is not powered, P-A is connected, B-S is connected, and R is blocked; When the solenoid valve is powered on, A-R is connected, P-B is connected, and S is blocked. The five way valve refers to a solenoid valve with five air pipe interfaces (A, B, R, P, S). The working principle of a two position five way solenoid valve is that the solenoid valve has a closed chamber with through holes at different positions, each hole leading to a different channel. The middle of the chamber is the piston, and there are two electromagnets on both sides. The magnetic coil on which side is energized will attract the piston to which side. By controlling the movement of the piston to block or leak out different holes, the piston drives the piston rod, which in turn drives the mechanical device to move. In this way, the mechanical motion is controlled by controlling the current of the electromagnet.View details>>